PESTS
ANTS
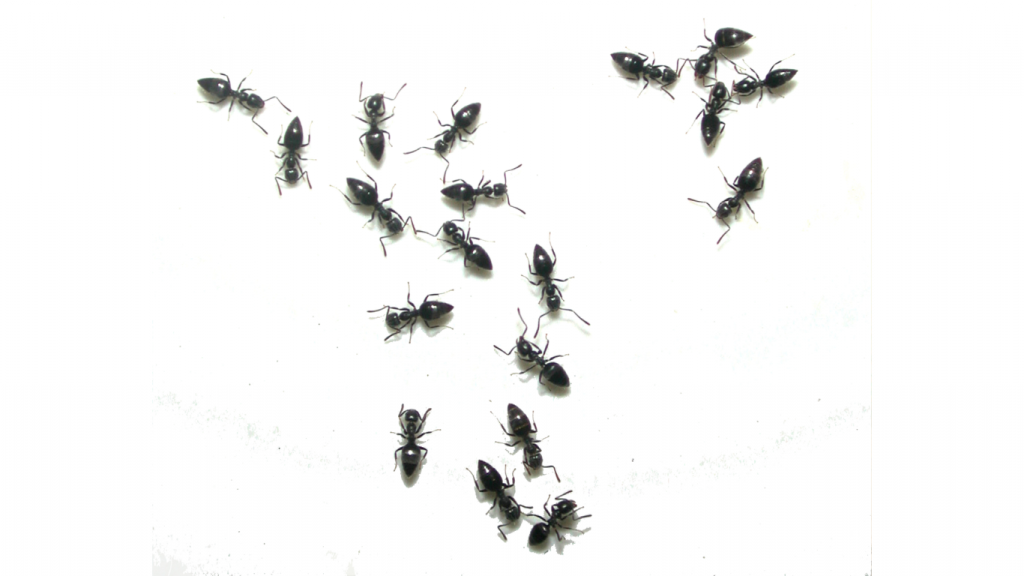

Facts
Type: Insect
Lifespan: Several weeks to several years
Size: 2 - 25 mm
Habitat: Ants thrive in most ecosystems, and may form 15–25% of the terrestrial biomass.
Facts cont'd
The most common species of ant in the UK, are the Garden Ant, Pharoah Ant, Roger's Ant and the Ghost Ant. Females are Larger than males. A queen ant can live longer than any other insect. Ants go through four stages of development: egg, larva, pupa and adult (metamorphosis). Most Ants will be their nests outside of the property with the exception of a few. The majority are simply visiting your kitchens, bathrooms and living rooms from outside where their nest is situated and are coming inside to look for food.
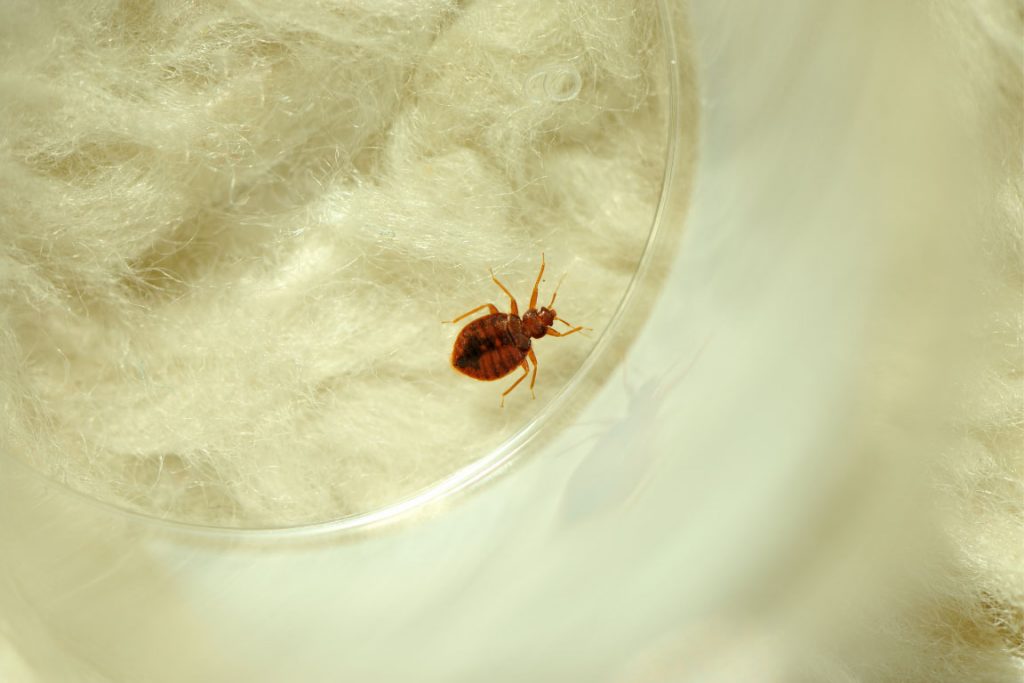
BEDBUGS
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: feed exclusively on blood
Size: Adults grow to 4–5 mm
Habitat: warm houses and especially near or inside beds and bedding
Range: worldwide
Scientific name: Cimex lectularius
Facts cont'd
Bed bugs are Parasitic insects that only feed on blood. The common bedbug prefers human blood. Bed bugs are mainly active at night, but are not exclusively nocturnal. A number of adverse health effects may result from bed bug bites, including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergic symptoms. Bed bugs use pheromones and kairomones to communicate regarding nesting locations, feeding, and reproduction. They obtain all the additional moisture they need from water vapour in the surrounding air. Bed bugs are attracted to their hosts primarily by carbon dioxide, secondarily by warmth, and also by certain chemicals.

COCKROACHES
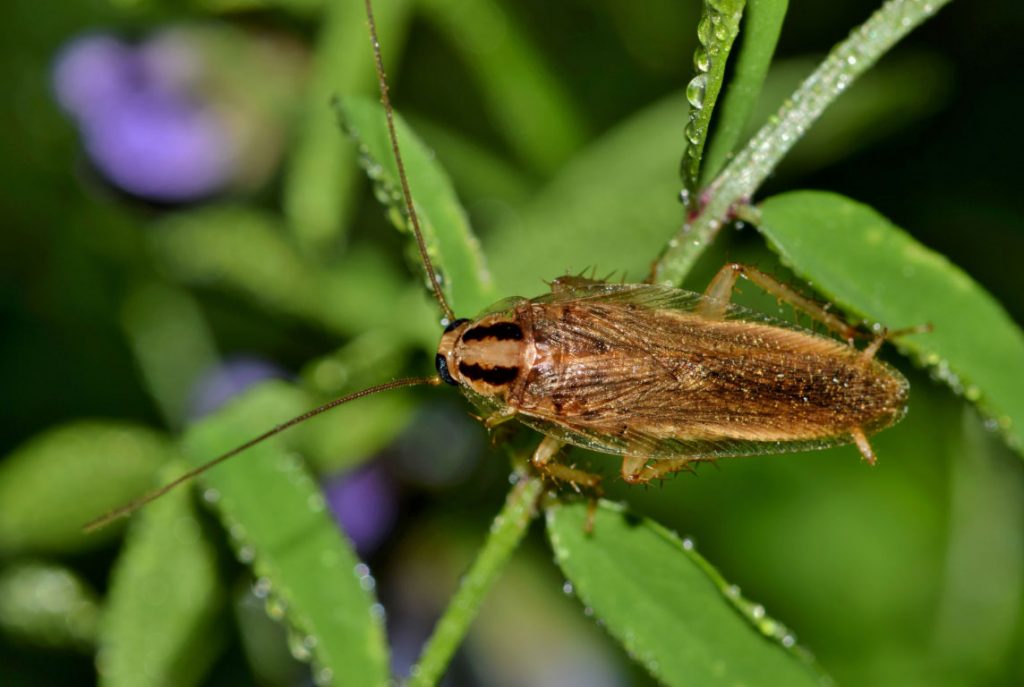

Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: sweets, meats and starches, hair, books and decaying matter. Anything and everything
Lifespan: German Cockroaches native to the UK 100 to 200 days.
Size: 3mm-80mm depending on species.
Weight: 0.1 and 0.12 g (German Cockroach)
Habitat: temperate, tropical, terrestrial
Range: Northern Hemisphere, native to Europe, Northern Africa, and temperate Asia.
Scientific name: Blattella germanica (German Cockroach)
Facts cont'd
The two main species of cockroaches in the UK are German Cockroaches and Oriental Cockroaches. Cockroaches are older than the dinosaurs and have walked the Earth for hundreds of millions of years. Cockroaches can survive for weeks without their head. They also require access to water, and will be generally found in inaccessible harbourages, close to water and food. Cockroaches can survive for several months without food, but will not live for more than a few days without water.
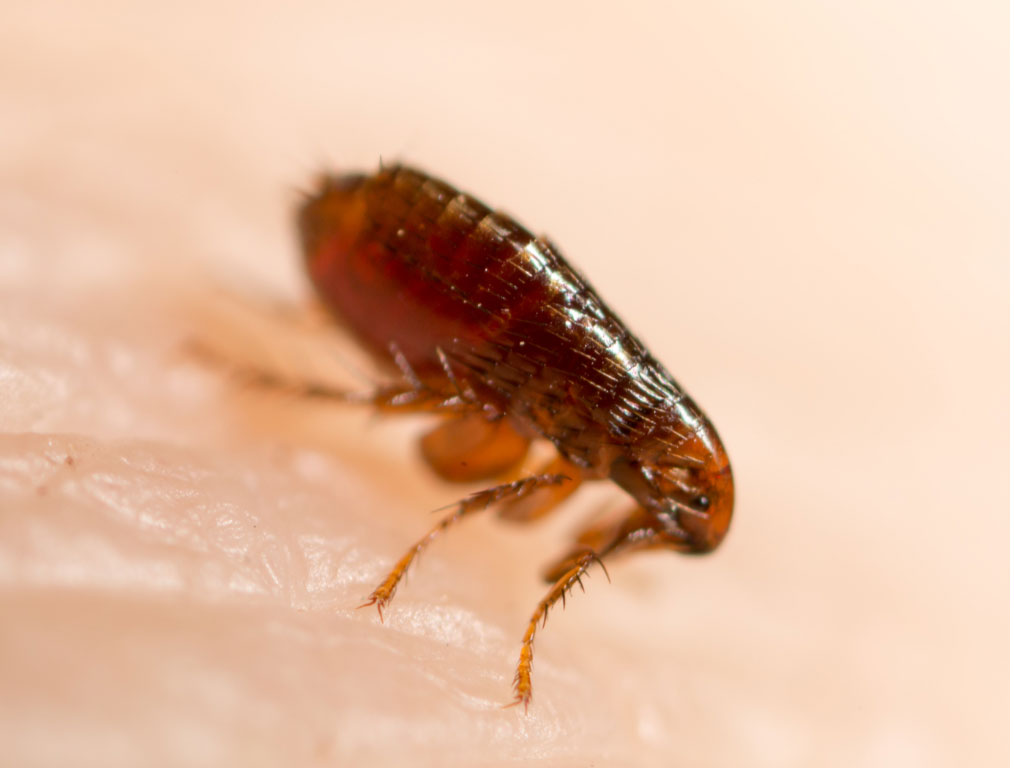
FLEAS
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: Blood
Lifespan: 2 to 4 months
Size: 1.5 – 3.3 mm long
Weight: 0.45 mg
Habitat: On the skin of warm-blooded animals.
Scientific name: Ctenocephalides
Facts cont'd
The most common species of flea is the Cat flea, well known for readily biting humans. Human Fleas are extremely rare. Flea populations are distributed with about 50% eggs, 35% larvae, 10% pupae, and 5% adults. Fleas are flightless, but very good at jumping, and once adult fleas emerge from pupae, they jump onto an unsuspecting passing animal host and start feeding on blood within minutes. Before feeding, fleas pump saliva onto the skin to prevent the blood from clotting. Proteins in this saliva can cause severe allergic reactions in your pet.

WASPS
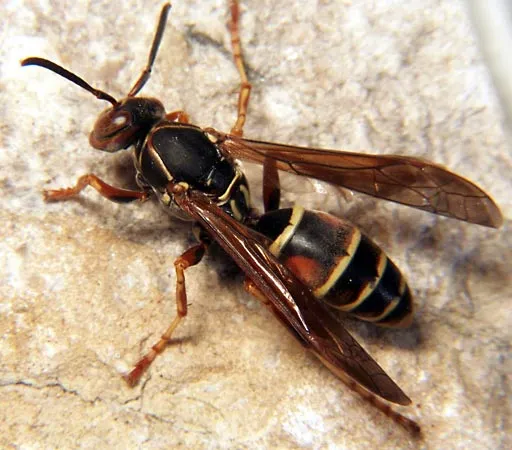

Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: Flies, aphids, caterpillars and other invertebrates
Lifespan: In social wasps, workers (sterile females) 12-22 days, drones have a slightly longer, and queens average 12 months
Size: up to 5cm depending on species
Weight: up to 0.8 g depending on species
Habitat: The Common wasp throughout the UK in almost all habitats, including woodland and urban areas nesting frequently inside homes and buildings.
Range: Northern Hemisphere, native to Europe, Northern Africa, and temperate Asia.South America (Argentina and Chile), Australia, and New Zealand.
Scientific name: Vespula vulgaris
Facts cont'd
Only female wasps have stingers and all worker wasps are female.
Potential queens and drones from the same nest use facial recognition to prevent cross-breeding. One nest may produce 30,000 wasps in a year. Worker wasps are all sterile females and will forage for over a mile in search of food. Their diet consists mainly of insects but during the months of August through October they have more of a taste for sugary delights from flowers and sweet substances resulting in them causing a nuisance to humans. Wasp stings are made up of an alkaline so an acid substance can be used to neutralise the pain.
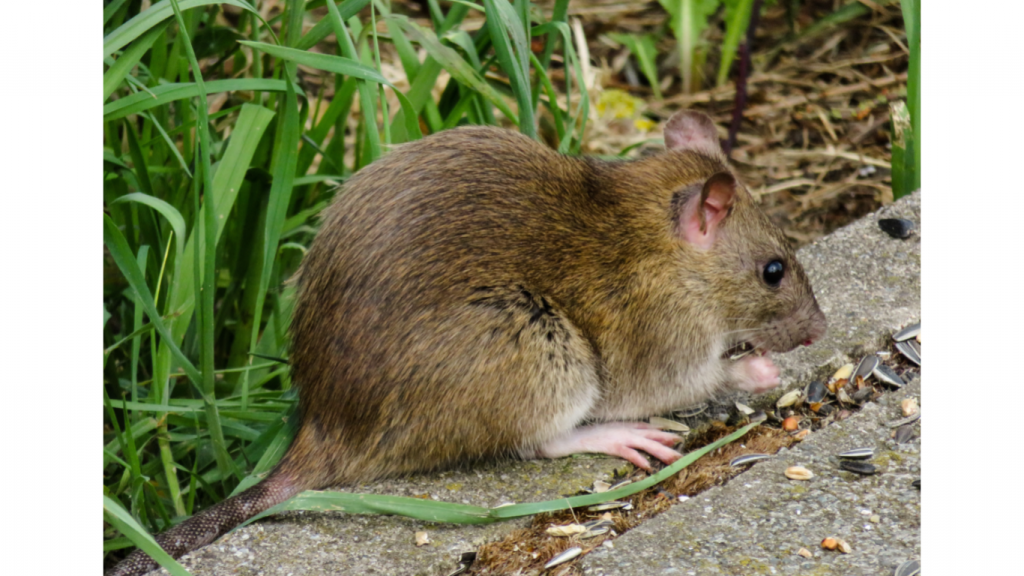
MICE
Facts
Type: Mammal (Rodent)
Diet: Predominantly herbivorous
Lifespan: Typically 1-2 years
Size: Body is 8-35 cm including tail
Weight: Average 30g
Habitat: Well adapted to various habitats
Range: Originated in Asia, but now common worldwide
Scientific name: Mus
Facts cont'd
Mice can carry diseases such as Salmonella, Hantavirus and Lyme Disease. They have an acute sense of hearing, frequently using ultrasound to communicate, and are particularly sensitive to any sudden noise and vibrations so will likely nest in cavity walls, loft spaces, and under floors that won’t have footsteps overhead (under stairs and wardrobes). Mice gnaw due to their front two top teeth (incisors) constantly growing which they file, grind and wear down by gnawing. Mice live for 2 to 3 months in the wild due to the harsh environment and amount of predators. In protected environments, however, they often live two to three years. They breed in early spring and autumn.
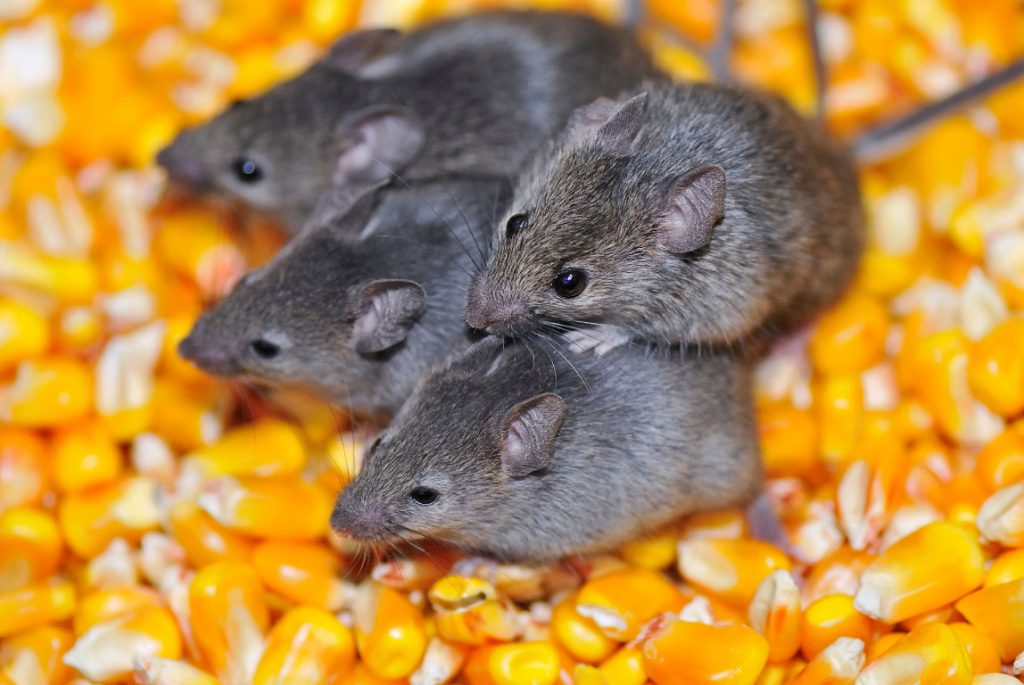

RATS
Facts
Type: Mammal (Rodent)
Diet: Omnivore
Lifespan: 2-3 years
Size: Average body is 25cm long with tail being a further 20cm
Weight: 350-450 g for females and 450-650 for males
Habitat: Extremely adaptable and can thrive in most habitats providing there is adequate food/water supply.
Range: Originated in Asia, but has spread throughout the world.
Scientific name: Rattus
Facts cont'd
The two types of rats common found in the UK are the Brown Rat and the Black Rat. Rat bites and scratches can cause disease and rat-bite fever, whilst the rats urine is responsible for the spread of leptospirosis (Weils Disease), which can in turn result in liver and kidney failure. One of the most historically dangerous rat-borne diseases is the bubonic plague, also called the “Black Plague’’. The disease is transferred when fleas from the rats bite human beings. Consuming food or water that is contaminated by the bacteria from rat feces can cause Salmonellosis (salmonella poisoning). They have an acute sense of hearing, frequently using ultrasound to communicate, and are particularly sensitive to any sudden noise. Both species breed rapidly and become sexually mature in about three months. Each female may produce from 3 to 12 litters of between six and eight young in a year.
FOXES
Facts
Type: Mammal
Diet: Carnivore
Lifespan: Average only 18 months to 2 years in the wild
Weight: Dogs, 5.9kg, Vixens, 5.2kg
Habitat: Very varied.
Range: Across the entire northern hemisphere from the Arctic Circle to North Africa, Central America, and the steppes of Asia. Its range has increased alongside human expansion.
Scientific name: Vulpes vulpes
Facts cont'd
Fox hunting with dogs is illegal in the UK. Foxes are part of the Canidae family, which means they’re related to wolves, jackals, and dogs. But unlike their relatives, foxes are not pack animals. Foxes are protected under a series of wildlife protection laws against poisoning, gassing, asphyxiating, maiming, stabbing, impaling, drowning, clubbing and most forms of snaring, with anyone carrying out such acts subject to 6 months imprisonment and/or £5,000 fine per animal. Up to 50 per cent of the UK’s fox population is killed on the roads. Up to 80 per cent of fox cubs die before reaching sexual maturity and therefore never breed. The majority of complaints involving urban foxes include digging holes in garden lawns and flower beds, fouling in gardens, biting through garden light cables and irrigation pipes, fouling in school playgrounds and digging holes in sports fields.
VARIED CARPET BEETLES
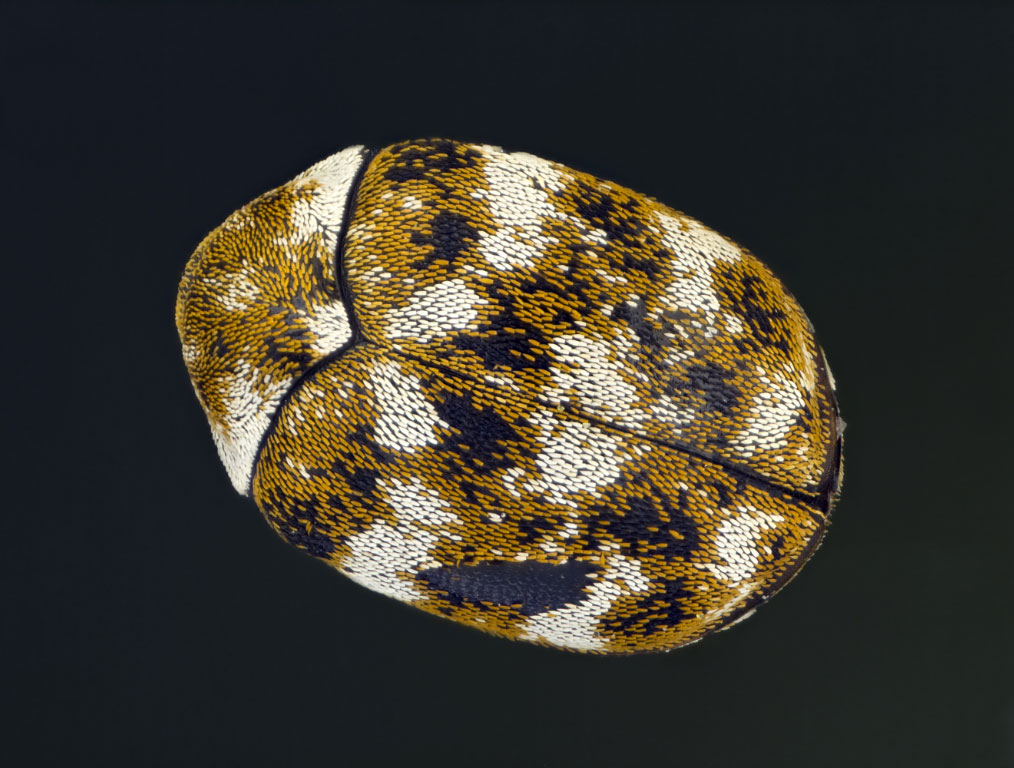
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: wool, fur, leather, and on plant fibers
Size: 0.08 to 0.2 in. (3–5 mm) long
Scientific name: Anthrenus verbasci
Facts cont'd
The adult Carpet Beetle feeds only on pollen and nectar of garden flowers but lays its eggs in old birds nests, felt, fabric or accumulated fluff in buildings. It is the larvae from these eggs that do the damage. They feed on feathers, fur, hair, or wool and tend to wander along the pipes from roofs into airing cupboards – which house the clothes and blankets which constitute the food. The larvae of the carpet beetle are known as woolly bears due to their hairy appearance. The larvae hide in dark, undisturbed areas and feed on organic material. Carpet beetles damage consists of fairly well-defined round holes along the seams of fabric where the grubs bite through the thread.
MOTHS
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: clothing and natural fibers; they have the ability to digest keratin protein in wool and silk
Lifespan: winged adults 3-16 days, larvae up to 2.5 years
Size: 1-1.5cm
Habitat: Near and around natural fabrics
Range: worldwide
Scientific name: Tineola bisselliella
Facts cont'd
The females tend to make small jumps and walk along surfaces while the males fly in search of a mate. Moths only fly when it is warm and tend to hide from light, keeping in dark corners where they lay eggs on wool, feathers or skins. Not only do moths munch away holes, but they also leave their silken cases, silken threads and faecal pellets all over the surface or your garment, which in turn provides new food sources for the next batch. Damage to articles may consist of irregular surface feeding or holes eaten completely through the fabric. Synthetic fabrics such as polyester and rayon are rarely attacked unless blended with wool. Clothing and blankets in constant use are seldom damaged by clothes moths, nor are rugs that get a normal amount of traffic or are routinely vacuumed. Cleaning kills any eggs or larvae that may be present and also removes perspiration odors that are attractive to the pests. Vacuuming effectively removes larvae which are already present as well as hair and lint which could support future infestations. Even piano or organ felts may be the source. Infested items should be thrown out, laundered or dry cleaned.
SILVERFISH
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: carbohydrates, particularly sugars and starches, cotton, dead insects, linen, silk.
Lifespan: two to eight years.
Size: 1-2cm
Habitat: temperate ; terrestrial
Range: urban ; suburban ; agricultural worldwide
Scientific name: Lepisma saccharina
Facts cont'd
Silverfish prefer dark and moist environments (75 – 97% humidity). Some of their preferred habitats are basements, kitchens, sinks, bathtubs, bookcases, wardrobe shelves, behind kickboards, wall cavities, and under floorboards Silverfish require a large supply of starchy foods or moulds to survive. Silverfish diets are high in protein, sugar, or starch, including cereals, moist wheat flour, starch in book bindings, and paper on which there is glue or paste. Silverfish are considered a nuisance pest because they feed on wallpaper pastes, natural textiles, books, and papers. Silverfish also feed on mould and fungus that grows on a variety of other surfaces. Silverfish are fast-moving and can travel throughout buildings. Once they find a good source of food, they stay close to it. Silverfish are nocturnal, but they are also active in dark areas throughout the structures they inhabit. They can be a problem all year round. You may see silverfish trapped in sinks and baths because they enter seeking moisture and are unable to climb the slippery vertical surface to escape.
WOODWORMS
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: wood
Habitat: various forest habitats
Scientific name: Artemisia absinthium
Facts cont'd
It is the round exit holes that normally identifies the timber that has been subjected to a beetle infestation. Once the adult male beetles have emerged from the chamber their sole purpose is to mate with as many female partners in their short lifespan so to produce future generations. These pests are seasonal like most other pests, and the woodworm season usually runs from May to October. The most common wood boring beetle found in British buildings is the Common Furniture Beetle. The wood boring beetle named the Deathwatch Beetle is an indigenous British insect. It prefers to munch on sapwood and heartwood of hardwoods, usually oak, which have partly decayed or are damp. Wood boring beetles can fly. Their flight is limited to some extent, but still enough to fly through open windows, as any other insect would do. The biggest risk of acquiring these pests is when purchasing old or second hand furniture. Ensure to inspect items carefully!!
BIRDS
Facts
Type: Bird
Diet: Omnivore
Lifespan: Average UK 2-5 years.
Size: 8.5cm-94cm (Goldcrest-White tailed eagle)
Weight: 4.5g-6.9kg (Goldcrest-White tailed eagle)
Habitat: Shore and sea, Rainforests, Desserts, Wetlands
Range: Worldwide
Scientific name: Aves
Facts cont'd
There have been cases of people becoming ill after prolonged exposure to dried bird droppings but, not only this, fresh bird droppings can be unsightly and slippery underfoot. Blue tits and great tits closely link their breeding with the emergence of caterpillars – great food for growing chicks. Parent birds deliver more than 10,000 to their young. In winter, tiny birds like wrens sleep together at night for warmth. Almost 9 million birds were counted as part of the 2004 RSPB Big Garden Birdwatch – that’s more than the combined human population of Scotland and Wales! Birds become a nuisance when they invade a property or surrounding space. Birds are normally welcome in gardens and woodlands across the UK but, like all other animals, birds and insects, should their numbers swell, with one species out doing another, the results for us can be unpleasant.
PIGEONS
Facts
Type: Bird
Diet: Omnivore
Lifespan: Up to years in the wild
Size: 31-34 cm, Wingspan 63-70 cm
Weight: Average 360g
Habitat: Urban areas
Range: Most cities around the world
Scientific name: Columba livia
Facts cont'd
Pigeons are monogamous and typically mate for life. Pigeons build a flimsy platform nest of straw and sticks, put on ledge, under cover, often located on the window ledges of buildings. In captivity, pigeons commonly live up to 15 years and sometimes longer. In urban populations, however, pigeons seldom live more than 3 or 4 years. Natural mortality factors, such as predation by mammals and other birds, diseases, and stress due to lack of food and water, reduce pigeon populations by approximately 30% annually. Pigeons are found to some extent in nearly all urban areas around the world. It is estimated that there are 400 million pigeons worldwide and that the population is growing rapidly together with increased urbanization. Sexes look nearly identical, although males are larger and have more iridescence on their neck. Juveniles are very similar in appearance to adults, but duller and with less iridescence. Pigeons are highly dependent on humans to provide them with food and sites for roosting, loafing, and nesting. They are commonly found around farm yards, grain elevators, feed mills, parks, city buildings, bridges, and other structures, although they can live anywhere where they have adequate access to food, water and shelter.
RABBITS
Facts
Type: Mammal
Diet: Herbivore
Lifespan: 1–9 years (wild); 7–10 years (captive)
Size: 8–20 in
Weight: 0.8 and 4.4 lb
Habitat: Meadows, woodland, forests, grasslands, deserts and wetlands
Range: North America, Europe, Southeast Asia, Africa and South America
Scientific name: Oryctolagus cuniculus
Facts cont'd
In the wild, rabbits live in warrens comprising an intricate series of underground tunnels or burrows with multiple entrances. Rabbits are burrowers and live in underground tunnel networks called warrens. Their whiskers are the same width as their body and are used to determine whether they will fit through a hole, which stops them from getting stuck in tunnels. Rabbits are sociable animals that live with other individuals in warrens. They are hierarchical, so one female rabbit is dominant; males will also form a hierarchy. The dominant rabbit enjoys many benefits. They get the best burrows, first dibs on food and can request grooming from other rabbits. Rabbits are prey animals. When out of the burrow, they are constantly on the lookout for predators, such as foxes. Once danger is detected, rabbits can signal to others by thumping their hind legs, before seeking the shelter of the burrow.
SEAGULLS
Facts
Type: Bird
Diet: Omnivore
Lifespan: 10-15 Years
Size: 30-75 cm
Weight: 120 – 1750 g
Habitat: Coastlines, bays, major lakes and urban areas
Range: Global
Scientific name: Laridae
Facts cont'd
It is illegal to remove a nest with young in it – usually between April and June Seagulls are attentive and caring parents. The male and female pair for life and they take turns incubating the eggs, and feeding and protecting the chicks. Gulls have a complex and highly developed repertoire for communication which includes a range of vocalisations and body movements. Seagulls are very clever. They learn, remember and even pass on behaviours, such as stamping their feet in a group to imitate rainfall and trick earthworms to come to the surface. Gulls have unhinging jaws which allow them to consume large prey. A small claw halfway up their lower leg enables them to sit and roost on high ledges without being blown off. Many seagulls have learned to conserve energy by hovering over bridges in order to absorb raising heat from paved roadways. Seagulls can drink both fresh and salt water. Most animals are unable to do this, but seagulls have a special pair of glands right above their eyes which is specifically designed to flush the salt from their systems through openings in the bill.
SQUIRRELS
Facts
Type: Mammal (Rodent)
Diet: Omnivore, although they are predominantly herbivorous
Lifespan: 2-5 years, with larger species tending to live longer
Size: 8-70 cm long depending on species
Weight: 10 g – 8 kg depending on species
Habitat: Adapted to a huge range of habitat from tropical rainforest to semiarid desert
Range: The Americas, Europe and Asia, with an introduced population in Australasia
Scientific name: Sciuridae
Facts cont'd
In Great Britain, Italy and Ireland, numbers have decreased drastically in recent years. This decline is associated with the introduction by humans of the eastern grey squirrel from North America and habitat loss. Due to this, without conservation the species could be extirpated from Britain by 2030 The Grey Squirrel carries the Pox Virus Parapoxvirus and this is usually fatal to red squirrels. Greys have developed an immunity to the disease having been exposed to the virus for many years. There is evidence, however, that some reds are also developing immunity to it. It is illegal to release a grey squirrel into the wild if captured, and should be disposed of by humane methods only. It is recommend that taking the animal to the vet to be put down for a fee or calling in pest control expert for culling. Grey squirrels eat a range of foods with a preference for shelled nuts of any sort, followed by seeds, berries, and other fruit.
BEES
Facts
Type: Insect
Diet: Herbivore
Lifespan: Western honey bee: 122 – 152 days
Size: 2-2.5 cm in length
Weight: Drone around 0.02 g, Workers between 0.04-0.60 g, Queen up to 0.85 g
Habitat: Meadows, parks and gardens
Range: Worldwide except arctic regions
Scientific name: Anthophila
Facts cont'd
Bees are not protected but they are considered to be in danger if current issue such as disease and carelessness continues. Treatment/disposal of the nest must be considered carefully. Bees are important for our echo system due to them being pollinators for flowers, fruits and vegetables. This means that they help other plants grow! Bees transfer pollen between the male and female parts, allowing plants to grow seeds and fruit. The average worker bee lives for just five to six weeks. During this time, shell produce around a twelfth of a teaspoon of honey. Sadly, over the past 15 years, colonies of bees have been disappearing, and the reason remains unknown. Referred to as colony collapse disorder, billions of Honey bees across the world are leaving their hives, never to return. In some regions, up to 90% of bees have disappeared

FLIES

Facts
Flies - House/Cluster/Blowflies
Type: Insect
Diet: Liquid or semi-liquid substances
Size: Adults range in length from 8–12 millimetres
Habitat Range: World Wide
Scientific name: Musca domestica
Facts cont'd
Over 100,000 species of flies live on earth. HOUSE FLIES TASTE WITH THEIR FEET. Flies don’t have teeth. Instead, they have a long tongue called a proboscis, which sucks up food like a straw. Some flies drink nectar or blood. House flies like the food we eat. When a fly lands on your lunch, it vomits on the food. Acids in the vomit dissolve the food so the fly can suck it up. Flies can be a serious risk to our health and have caused many deaths in the past. Flies carry disease and during the Spanish-American War, 5,000 soldiers died from typhoid, a disease spread by flies. Only 4,000 soldiers actually died in battle.







